How do you install a power usage monitor? Without mayor changes to your distribution panel?
Well, simply clamp a split-coil current transformer like the
SCT013-000
in the picture onto the electric cable
to be measured.
So far so good. The current transformer generates a current in the secondary coil that is proportional to the
current going through the primary coil which is proportional to the
apparent power
usage, assuming a resistive load.
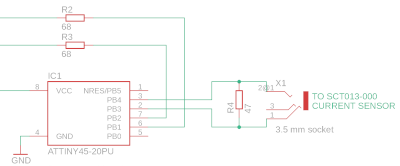
The challenge is to measure the current and make it available through USB.
The first step is to convert the current to a voltage by connecting a load resistor to the secondary coil.
Unfortunately the result is an AC voltage, which is more difficult to measure than DC.